

Many natural compounds like resveratrol and berberine also activate AMPK by changing the nucleotide ratio. AICAR (5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleoside) which mimics AMP thereby activates AMPK whereas metformin activates AMPK by increasing the ratio of AMP/ATP. In the past, attempts were made to activate AMPK either directly or indirectly in order to get the potential benefit to manage the metabolic syndrome. Apart from its role in metabolism, it is known that AMPK activation is anti-inflammatory and exerts immunosuppressive effects in different cells. In the skeletal muscle, both leptin and adiponectin activates AMPK whereas exercise mediated AMPK activation depends on local signaling pathways. In the adipose tissue, AMPK activation has a direct negative impact on lipolysis through phosphorylation of HSL at Ser 565 and ATGL at Ser 406. In liver, AMPK activation reduces cholesterol synthesis by inhibiting HMGCR. Impaired AMPK activation is associated with reduced mitochondrial function and dysregulated intracellular lipid metabolism. AMPKα2 deletion has shown to reduce insulin sensitivity, impaired glucose tolerance along with defects in insulin secretion. It is well established that AMPK activity is reduced in the diabetic or metabolic syndrome condition. It is known by recent findings that AMPK heterotrimer changes its distribution and localization between cytoplasm and nucleus with the help of nuclear export sequence in the catalytic subunit of AMPK. Upon phosphorylation, AMPK drives multiple cellular signaling pathways which can be antagonized by dephosphorylation with protein phosphatases. ĪMPK activation happens in the cell under the low energy conditions (decrease in ATP and increase in AMP). The initiation of AMPK activation occurs when AMP binds to the γ regulatory subunit followed by conformational changes in α, β and γ. The phosphorylation of threonine 172 (Thr 172) at alpha subunit is necessary for activation of AMPK. The predominant heterotrimer combination varies from tissue to tissue. It is a heterotrimer comprising of a catalytic α, regulatory β and γ subunits. It also reduces body weight gain with an additional benefit of minimizing cardiovascular risks in diabetics.ĪMP- activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) a serine/threonine protein kinase has been postulated as an important drug target in metabolic syndrome and diabetes because of its role in regulation of cellular energy metabolic homeostasis. ConclusionsĬNX-012-570 has the potential to control hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia. There was significant reduction in liver TG and liver total cholesterol. Body weight was reduced by 13% with increased browning of adipose tissue and decreased inguinal and mesenteric fat mass. Decrease in serum insulin and glucose AUC indicates the increased insulin sensitivity. In db/db mice model, CNX-012-570 has shown 18% decrease in fed glucose and 32% decrease in fasting glucose with a 2.57% reduction in absolute HbA1c. CNX-012-570 showed a 22% reduction in fed serum cholesterol levels and 19% increase in HDL levels. CNX-012-570 has reduced fasting blood glucose levels by 14%, body weight by 24% and fasting serum triglycerides (TG) by 24%. The efficacy of the molecule was translated to both DIO and db/db animal models of diabetes.
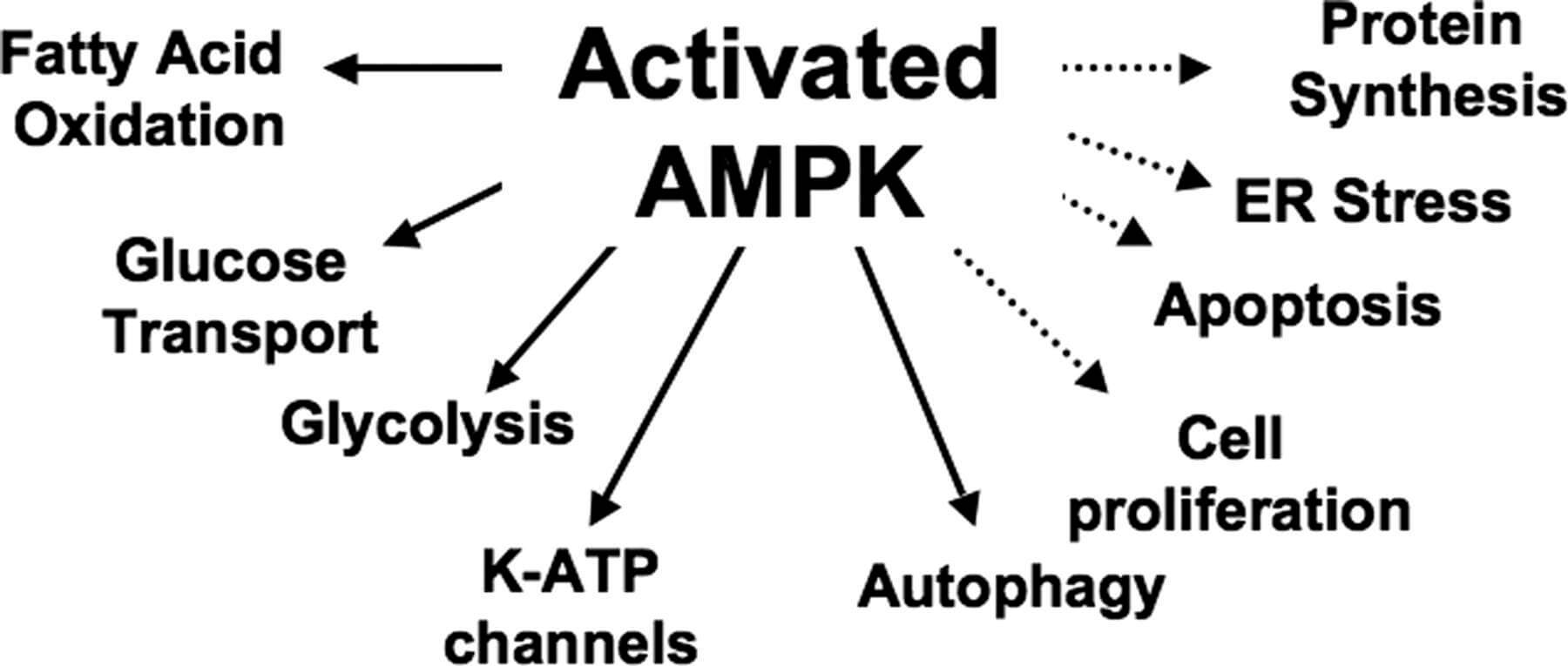
It inhibits lipolysis (33%) and gluconeogenesis (28%) in 3T3L1 cells and rat primary hepatocytes respectively.
Ampk metabolic activator free#
ResultsĬNX-012-570 is a highly potent and orally bioavailable compound activating AMPK in both cell and cell free systems. Genetically diabetic db/db mice on chow diet were dosed with vehicle control or CNX-012-570 (2.5 mg/kg, orally once a day) for 6 weeks (n = 8). Male C57BL/6 mice fed with high fat diet (HFD) were assigned to either vehicle or CNX-012-570 (3 mg/kg, orally once a day) for 8 weeks (n = 8). MethodsĪctivity and efficacy of the compound was tested in cell based as well as cell free systems in vitro. We report the anti-hyperglycemic and anti-hyperlipidemic effects of CNX-012-570 is an orally bioavailable small molecule (molecular weight of 530 Daltons) that directly activates AMPK in DIO and db/db animal models of diabetes. AMP activated protein kinase (AMPK) regulates the coordination of anabolic and catabolic processes and is an attractive therapeutic target for T2DM, obesity and metabolic syndrome.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
